This tutorial is designed for macOS or BSD systems.
What is kqueue?
kqueue is an event notification mechanism in macOS (and BSD systems such as FreeBSD).
If you are writing a server, but you don’t want to allocate a thread for each client;
you can use kqueue to listen for events from clients, for example:
- Who just connected?
- Who disconnected?
- Which client has sent a message?
The system notifies you automatically. Multiple clients can be served by a single thread.
This is I/O Multiplexing. kqueue is similar to epoll in Linux and iocp in Windows.
This will save resources.
How to use kqueue?
We need define a base code struct.
#ifdef __APPLE__
// Write code to use kqueue
#endif
int main() {
#ifdef __APPLE__
// init socket
#endif
return 0;
}
This is a client/server architecture, and the first thing we need to do is define the list of clients.
fdrepresents a file descriptor. It is similar to phone number.
#define MAX_CLIENT_QTY 1024
struct client_data
{
// If client_data[i].fd > 0, this isn't empty
// If client_data[i].fd == 0, this is empty
int fd;
} client_data[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
The socket server needs to be initialized before use.
Open and listen a port (Now, we are listening 127.0.0.1:25560).
int socket_listen()
{
// Define address info data structure
struct addrinfo *addr;
struct addrinfo hints;
// Reset memory data to 0
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints));
// AI_PASSIVE: This is a server address
hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE;
// PF_UNSPEC: No protocol family specified, IPv4 or IPv6
hints.ai_family = PF_UNSPEC;
// SOCK_STREAM: Use TCP byte stream
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM;
// 127.0.0.1: Only allow local address
// 25560: Port number
getaddrinfo("127.0.0.1", "25560", &hints, &addr);
// ai_family: Protocol family
// ai_socktype: Socket type, is SOCK_STREAM
// ai_protocol: Protocol number, 0 -> TCP
// This line code indicates that a doorknob is being added to the "port" door
const int socket_s = socket(addr->ai_family, addr->ai_socktype, addr->ai_protocol);
// Give the "socket" door a house number
bind(socket_s, addr->ai_addr, addr->ai_addrlen);
// There are 5 chairs lined up at the entrance; if too many new clients arrive, they'll have to wait
listen(socket_s, 5);
// Return the handle of this socket
return socket_s;
}
Start listener.
int socket_init()
{
// Initialize the handle of socket
const int socket_s = socket_listen();
// Create an event listener queue
const int kq = kqueue();
// Create an event
struct kevent kev;
// kev: Event struct
// socket_s: the file descriptor (or handle) of socket
// EVFILT_READ: Listen for "readable events" (new connection or data arrival)
// EV_ADD: Add this event to kqueue
// Other parameters use default value (0 or NULL)
// This line code mean: Call me when someone comes
EV_SET(&kev, socket_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
// Registry event
// kq: Queue
// kev: Event
// 1: Event quatity
// Other parameters: Only registry
kevent(kq, &kev, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
// Start event listener loop (To be implemented later)
// "Waiters begin working 24/7"
run_event_loop(kq, socket_s);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Implement event listener loop.
void run_event_loop(const int kq, const int socket_s)
{
// `evs`: A temporary variable used to register or remove events from `kqueue`
struct kevent evs;
// `addr` and `addr_len`: Used to store client address information (used during `accept()`)
struct sockaddr_storage addr;
socklen_t addr_len = sizeof(addr);
// Infinite loop listening for events
while (1)
{
struct kevent events[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
// The server (program) arrives at the main service desk (kq), s
// tands still (permanently blocked), and waits for a customer (file descriptor/signal)
// to call for service (an event occurs).
// Once a call occurs, the service desk records all past call information,
// up to a maximum of the number of pages in the logbook (MAX_CLIENT_QTY),
// into your logbook (the `events` array), and then tells you the total number
// of calls recorded (ne).
const int ne = kevent(kq, NULL, 0, events, MAX_CLIENT_QTY, NULL);
// Iterate through each event
for (int i = 0; i < ne; ++i)
{
// New connect event
if (events[i].ident == socket_s)
{
// Accept connection
const int clint_s = accept(events[i].ident, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, &addr_len);
// Successfully: Add clint_s to the list of clients (To be implemented later)
if (create_connect(clint_s) == 0)
{
// Registry event to kqueue
EV_SET(&evs, clint_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &evs, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
// Send welcome message to the client (To be implemented later)
send_welcome_msg(clint_s);
}
// Failed
else
{
printf("accept error");
// Close connection
close(clint_s);
}
}
// Client disconnect
else if (events[i].flags & EV_EOF)
{
// Get file descriptor
const int fd = events[i].ident;
printf("fd %d closed\n", fd);
// Remove event from kqueue
EV_SET(&evs, fd, EVFILT_READ, EV_DELETE, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &evs, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
// Clear the client from the list of client (To be implemented later)
remove_connect(fd);
}
// Client sent message
else if (events[i].filter == EVFILT_READ)
{
// Receive message (To be implemented later)
recv_msg(events[i].ident);
}
}
}
}
Get connect by fd
int get_connect(const int fd)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
if (client_data[i].fd == fd)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int get_empty_connect()
{
// 0: 0 is empty connect
// Find first empty connect location
return get_connect(0);
}
Create connect and insert into the list of client.
int create_connect(const int fd)
{
// Check if fd is valid
// fd > 0 -> valid
// fd <= 0 -> invalid
if (fd <= 0)
{
// Failed
return -1;
}
// Get empty connect
const int res = get_empty_connect();
// If full
if (res == -1)
{
// Failed
return -1;
}
// Not full
client_data[res].fd = fd;
return 0;
}
Send welcome message to client.
// s: client number or fd
void send_welcome_msg(const int s)
{
char msg[80];
sprintf(msg, "welcome! you are client #%d!\n", get_connect(s));
// Send message to the the client
// s: client number or fd
// msg: Message content
// strlen(msg): the length of the message content
// 0: default send method
send(s, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
}
Remove connect from the list of client.
int remove_connect(const int fd)
{
if (fd <= 0)
{
return -1;
}
const int res = get_connect(fd);
if (res == -1)
{
return -1;
}
// Set 0 to clear the client
client_data[res].fd = 0;
return 0;
}
Receive message.
void recv_msg(const int s)
{
// Create a memory buffer, max 1023 byte (0 - 1022), because buf[1023] is '\0'
char buf[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
// Read data from socket
// Max size: buf length - 1
// 0: default read method
// bytes_read: the number of bytes actually read
const int bytes_read = recv(s, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 0);
// Append '\0'
buf[bytes_read] = 0;
printf("client #%d: %s", get_connect(s), buf);
// Force the output to be printed to the screen immediately
fflush(stdout);
}
Now you can use kqueue in a basic way.
Extended content.
How can we obtain input from stdin and implement the corresponding functionality?
Since we need to perform some string operations here, we need to create some functions first.
These are not the focus of this discussion, so they will not be covered for now.
int start_with(const char *prefix, const char *str)
{
size_t prefix_len = strlen(prefix);
size_t str_len = strlen(str);
return str_len < prefix_len ? 0 : !memcmp(prefix, str, prefix_len);
}
char** split_by_space(const char *str) {
char *copy = strdup(str);
char *token = strtok(copy, " ");
int capacity = 10;
char **result = malloc(capacity * sizeof(char*));
int count = 0;
while (token) {
if (count >= capacity - 1) {
capacity *= 2;
result = realloc(result, capacity * sizeof(char*));
}
result[count++] = strdup(token);
token = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
result[count] = NULL;
free(copy);
return result;
}
char* str_replace(const char *src, const char *old, const char *new_str) {
if (!src || !old || !new_str) return NULL;
size_t src_len = strlen(src);
size_t old_len = strlen(old);
size_t new_len = strlen(new_str);
if (old_len == 0) return strdup(src);
size_t count = 0;
const char *pos = src;
while ((pos = strstr(pos, old)) != NULL) {
count++;
pos += old_len;
}
size_t new_total_len = src_len + (new_len - old_len) * count + 1;
char *result = malloc(new_total_len);
if (!result) return NULL;
const char *src_ptr = src;
char *dst_ptr = result;
while ((pos = strstr(src_ptr, old)) != NULL) {
size_t bytes_to_copy = pos - src_ptr;
memcpy(dst_ptr, src_ptr, bytes_to_copy);
dst_ptr += bytes_to_copy;
memcpy(dst_ptr, new_str, new_len);
dst_ptr += new_len;
src_ptr = pos + old_len;
}
strcpy(dst_ptr, src_ptr);
return result;
}
How to read stdin async? (Or why we need to read async?)
Based on the previous code, we know that the run_event_loop
function is an infinite loop function and cannot block the
run_event_loop loop. Therefore, we cannot read it in
the conventional way, but can only read it async.
Q: So how do we implement asynchronous reading?
A: It’s very simple, we can use multithreading to read.
Let’s first create an empty function.
void *stdin_reader()
{
// Write code
}
Modify the code in the socket_init function.
Before:
int socket_init()
{
const int socket_s = socket_listen();
const int kq = kqueue();
struct kevent kev;
EV_SET(&kev, socket_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &kev, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
run_event_loop(kq, socket_s);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
After:
int socket_init()
{
const int socket_s = socket_listen();
const int kq = kqueue();
struct kevent kev;
EV_SET(&kev, socket_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &kev, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
// Create a handle of thread
pthread_t ptr;
// Create a new thread
// &ptr: a handle of thread
// NULL: default thread attr
// stdin_reader: this is the function we want to use to read `stdin`
// NULL: the parameters passed to `stdin_reader` are not needed here
pthread_create(&ptr, NULL, stdin_reader, NULL);
// Infinite loop
run_event_loop(kq, socket_s);
// End of the thread
pthread_cancel(ptr);
// Waiting for the thread to finish (reclaim resources)
pthread_join(ptr, NULL);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Complete stdin_reader function.
void send_all_msg(const char *msg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
if (client_data[i].fd > 0)
{
send(client_data[i].fd, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
}
}
}
void *stdin_reader()
{
// Memeory buffer, max 256 byte
char s[256];
// Use `fgets()` to read an entire line from stdin (keyboard)
// Tips: In operating systems like Linux and BSD, there is an important concept - everything is a file,
// so, stdin is a file.
while (fgets(s, sizeof(s), stdin))
{
// Append '\0' to s
s[strcspn(s, "\n") + 1] = 0;
// Check if s is "/quit\n"
if (strcmp(s, "/quit\n") == 0)
{
// Execute quit function
exit(0);
}
// Check if s is "/help\n"
if (strcmp(s, "/help\n") == 0)
{
// Output help info
printf("Available commands:\n");
printf("/help - Show this help message\n");
printf("/quit - Quit the server\n");
printf("/say <client_id> <message> - Send a message to a specific client\n");
printf("/list - List all connected clients\n");
continue;
}
// Check if s is start with "/list"
if (start_with("/list", s))
{
printf("Connected clients:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
// Output all exists clients
if (client_data[i].fd > 0)
{
printf("#%d\n", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
continue;
}
// Check if s is start with "/say"
if (start_with("/say", s))
{
// Split s by space
char** tokens = split_by_space(s);
// Get tokens length
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; tokens[i] != NULL; i++)
{
count++;
}
// Check if count is lt 3
if (count < 3)
{
// Output help info
printf("Usage: /say <client_id> <message>\n");
continue;
}
// Get and check client id
int client_id = atoi(tokens[1]);
if (client_id < 0 || client_id >= MAX_CLIENT_QTY)
{
printf("Invalid client id\n");
continue;
}
// Get command header, for example:
// /say 0 Hello, I am a server.
// Command header is "/say 0 "
char* cmd_header = strcat(strcat(tokens[0], " "), strcat(tokens[1], " "));
// Clear command header to get all message content
char* msg = str_replace(s, cmd_header, "");
// Send message to the client
send(client_data[client_id].fd, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
// Free pointer
free(tokens);
}
else
{
send_all_msg(s);
}
}
return NULL;
}
The complete code.
#ifdef __APPLE__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <_stdlib.h>
#include <sys/event.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define MAX_CLIENT_QTY 1024
struct client_data
{
int fd;
} client_data[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
int get_connect(const int fd)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
if (client_data[i].fd == fd)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int get_empty_connect()
{
return get_connect(0);
}
int create_connect(const int fd)
{
if (fd <= 0)
{
return -1;
}
const int res = get_empty_connect();
if (res == -1)
{
return -1;
}
client_data[res].fd = fd;
return 0;
}
int remove_connect(const int fd)
{
if (fd <= 0)
{
return -1;
}
const int res = get_connect(fd);
if (res == -1)
{
return -1;
}
client_data[res].fd = 0;
return 0;
}
void recv_msg(const int s)
{
char buf[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
const int bytes_read = recv(s, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 0);
buf[bytes_read] = 0;
printf("client #%d: %s", get_connect(s), buf);
fflush(stdout);
}
void send_welcome_msg(const int s)
{
char msg[80];
sprintf(msg, "welcome! you are client #%d!\n", get_connect(s));
send(s, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
}
void send_all_msg(const char *msg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
if (client_data[i].fd > 0)
{
send(client_data[i].fd, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
}
}
}
void run_event_loop(const int kq, const int socket_s)
{
struct kevent evs;
struct sockaddr_storage addr;
socklen_t addr_len = sizeof(addr);
while (1)
{
struct kevent events[MAX_CLIENT_QTY];
const int ne = kevent(kq, NULL, 0, events, MAX_CLIENT_QTY, NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < ne; ++i)
{
if (events[i].ident == socket_s)
{
const int clint_s = accept(events[i].ident, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, &addr_len);
if (create_connect(clint_s) == 0)
{
EV_SET(&evs, clint_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &evs, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
send_welcome_msg(clint_s);
} else
{
printf("accept error");
close(clint_s);
}
}
else if (events[i].flags & EV_EOF)
{
const int fd = events[i].ident;
printf("fd %d closed\n", fd);
EV_SET(&evs, fd, EVFILT_READ, EV_DELETE, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &evs, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
remove_connect(fd);
}
else if (events[i].filter == EVFILT_READ)
{
recv_msg(events[i].ident);
}
}
}
}
int start_with(const char *prefix, const char *str)
{
size_t prefix_len = strlen(prefix);
size_t str_len = strlen(str);
return str_len < prefix_len ? 0 : !memcmp(prefix, str, prefix_len);
}
char** split_by_space(const char *str) {
char *copy = strdup(str);
char *token = strtok(copy, " ");
int capacity = 10;
char **result = malloc(capacity * sizeof(char*));
int count = 0;
while (token) {
if (count >= capacity - 1) {
capacity *= 2;
result = realloc(result, capacity * sizeof(char*));
}
result[count++] = strdup(token);
token = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
result[count] = NULL;
free(copy);
return result;
}
char* str_replace(const char *src, const char *old, const char *new_str) {
if (!src || !old || !new_str) return NULL;
size_t src_len = strlen(src);
size_t old_len = strlen(old);
size_t new_len = strlen(new_str);
if (old_len == 0) return strdup(src);
size_t count = 0;
const char *pos = src;
while ((pos = strstr(pos, old)) != NULL) {
count++;
pos += old_len;
}
size_t new_total_len = src_len + (new_len - old_len) * count + 1;
char *result = malloc(new_total_len);
if (!result) return NULL;
const char *src_ptr = src;
char *dst_ptr = result;
while ((pos = strstr(src_ptr, old)) != NULL) {
size_t bytes_to_copy = pos - src_ptr;
memcpy(dst_ptr, src_ptr, bytes_to_copy);
dst_ptr += bytes_to_copy;
memcpy(dst_ptr, new_str, new_len);
dst_ptr += new_len;
src_ptr = pos + old_len;
}
strcpy(dst_ptr, src_ptr);
return result;
}
void *stdin_reader()
{
char s[256];
while (fgets(s, sizeof(s), stdin))
{
s[strcspn(s, "\n") + 1] = 0;
if (strcmp(s, "/quit\n") == 0)
{
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
if (start_with("/help", s))
{
printf("Available commands:\n");
printf("/help - Show this help message\n");
printf("/quit - Quit the server\n");
printf("/say <client_id> <message> - Send a message to a specific client\n");
printf("/list - List all connected clients\n");
continue;
}
if (start_with("/list", s))
{
printf("Connected clients:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CLIENT_QTY; i++)
{
if (client_data[i].fd > 0)
{
printf("#%d\n", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
continue;
}
if (start_with("/say", s))
{
char** tokens = split_by_space(s);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; tokens[i] != NULL; i++)
{
count++;
}
if (count < 3)
{
printf("Usage: /say <client_id> <message>\n");
continue;
}
int client_id = atoi(tokens[1]);
if (client_id < 0 || client_id >= MAX_CLIENT_QTY)
{
printf("Invalid client id\n");
continue;
}
char* cmd_header = strcat(strcat(tokens[0], " "), strcat(tokens[1], " "));
char* msg = str_replace(s, cmd_header, "");
send(client_data[client_id].fd, msg, strlen(msg), 0);
free(tokens);
}
else
{
send_all_msg(s);
}
}
return NULL;
}
int socket_listen()
{
struct addrinfo *addr;
struct addrinfo hints;
memset(&hints, 0, sizeof(hints));
hints.ai_flags = AI_PASSIVE;
hints.ai_family = PF_UNSPEC;
hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM;
getaddrinfo("127.0.0.1", "25560", &hints, &addr);
const int socket_s = socket(addr->ai_family, addr->ai_socktype, addr->ai_protocol);
bind(socket_s, addr->ai_addr, addr->ai_addrlen);
listen(socket_s, 5);
return socket_s;
}
int socket_init()
{
const int socket_s = socket_listen();
const int kq = kqueue();
struct kevent kev;
EV_SET(&kev, socket_s, EVFILT_READ, EV_ADD, 0, 0, NULL);
kevent(kq, &kev, 1, NULL, 0, NULL);
pthread_t ptr;
pthread_create(&ptr, NULL, stdin_reader, NULL);
run_event_loop(kq, socket_s);
pthread_cancel(ptr);
pthread_join(ptr, NULL);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
int main() {
#ifdef __APPLE__
socket_init();
#endif
return 0;
}
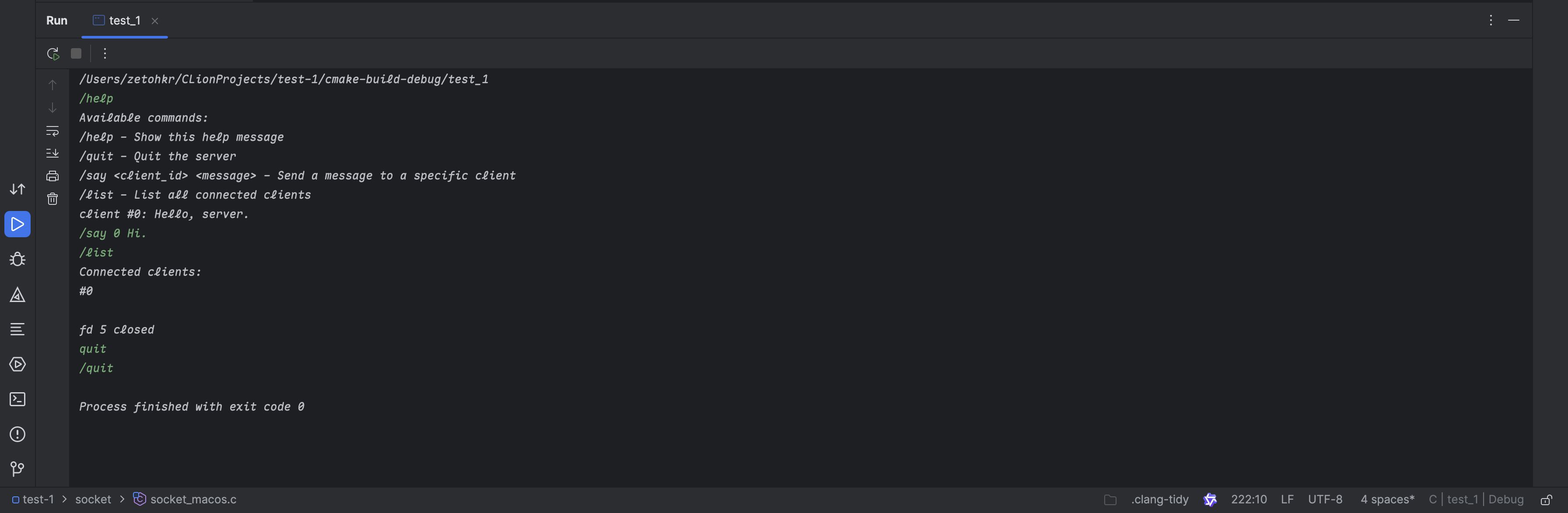
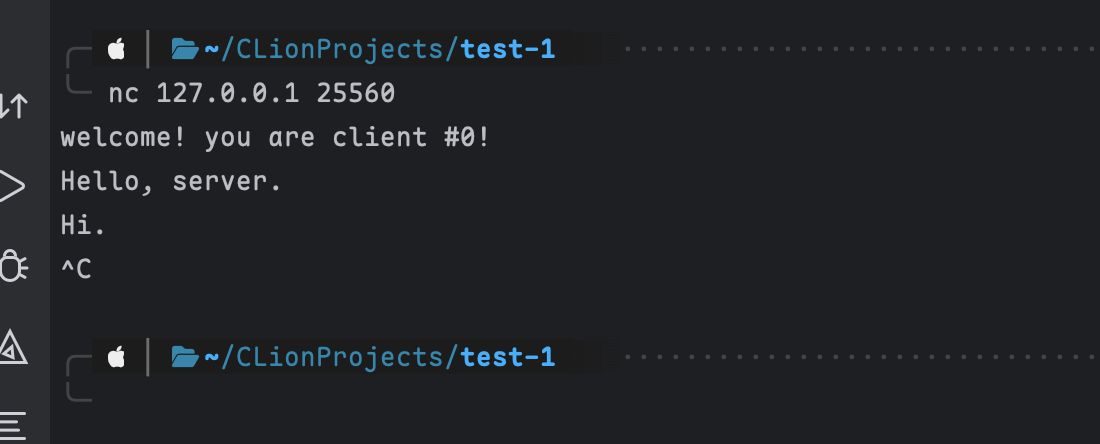
Screenshot of running.