First of all, this is just a tutorial, there is no complete code.
Overview
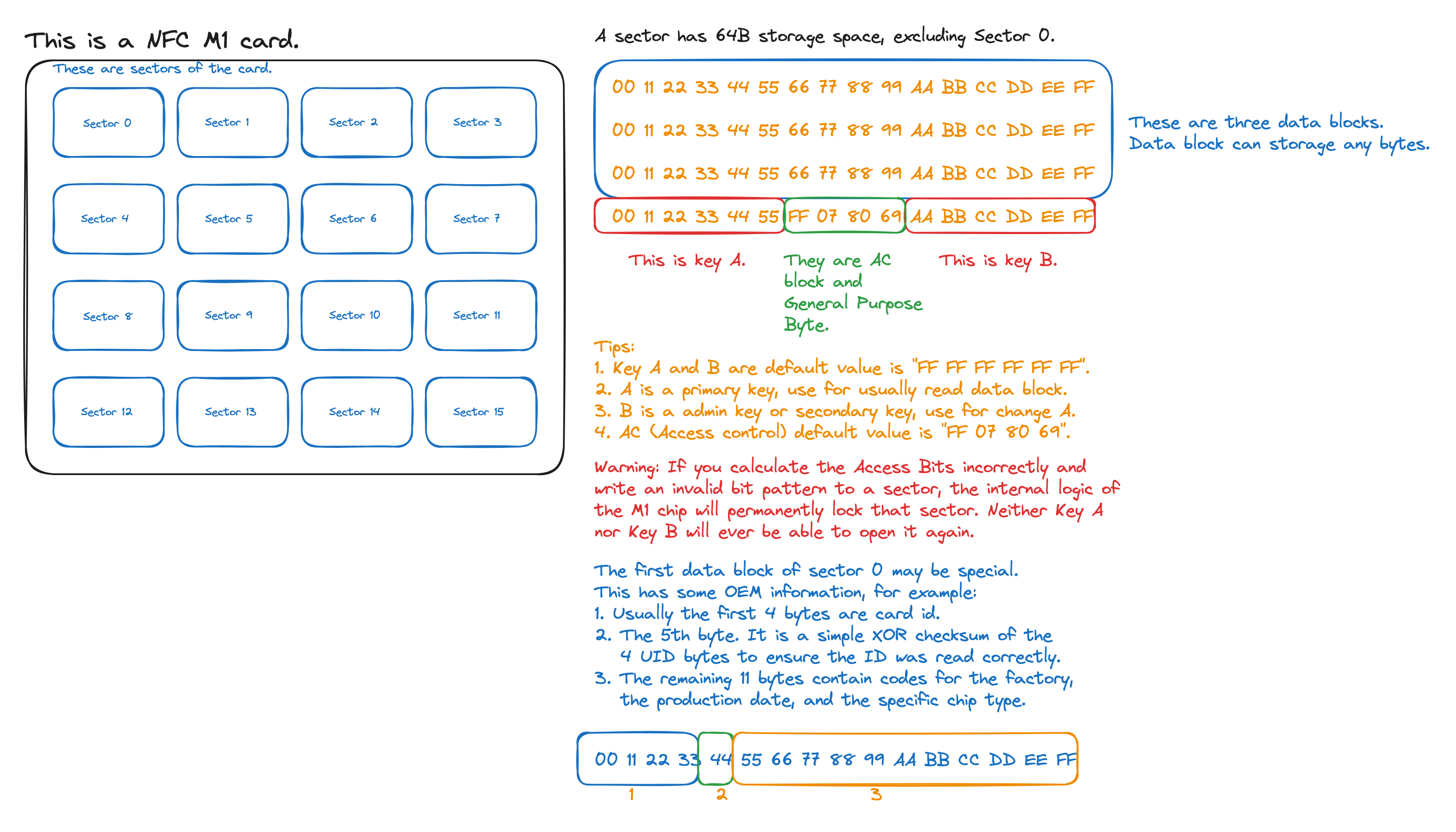
What is the NFC M1 card?
The NFC M1 is a passive RFID/NFC card produced by NXP Semiconductors.
- It has 1 KB of storage, divided into 16 sectors.
- It operates at 13.56 MHz (High Frequency), which is the standard frequency for NFC.
- It follows the ISO/IEC 14443-A(Type-A) protocol.
For example diagram:
Read Card
How to read card in Android?
- First, you should have a android phone of NFC function.
- You must be enable NFC in your android phone.
- A empty or useless card.
Let’s write code.
AndroidManifest.xml
- Request permissions
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.NFC" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.nfc" android:required="true" />
MainActivity.kt
- Define a NFC adapter:
private var nfcAdapter: NfcAdapter? = null,NfcAdapterisandroid.nfc.NfcAdapter - Init NFC adapter in
MainActivity#onCreatemethod:this.nfcAdapter = NfcAdapter.getDefaultAdapter(this) - Create a override method(For example):
If you need to read cards from other SAKs or card models, you will need to write the corresponding multi-branch conditions yourself.
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent)
{
super.onNewIntent(intent)
if (NfcAdapter.ACTION_TECH_DISCOVERED == intent.action) {
val tag: Tag? = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU) {
intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG, Tag::class.java)
} else {
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG)
}
val nfcA = NfcA.get(tag)
when (nfcA.sak.toInt()) {
0x08, 0x18 -> {
val mfc = MifareClassic.get(tag)
// A connection must be established before operation
// In Kotlin's `onNewIntent` method, `mfc.connect()` should be placed in a `try-catch` block. NFC connections are very unstable; an `IOException` is easily thrown when the card is brought near or moved away.
mfc.connect()
// Read sector 0 to 1
for (i in 0..1) {
// Here use default key "FF FF FF FF FF FF", if u want to use other key, u need change it.
val successA = mfc.authenticateSectorWithKeyA(i, MifareClassic.KEY_DEFAULT)
val successB = mfc.authenticateSectorWithKeyB(i, MifareClassic.KEY_DEFAULT)
if (successA || successB) {
val fstBlkIdx = mfc.sectorToBlock(i)
val lstBlkIdx = fstBlkIdx + 3
// Read data block 0 to 3
for (blockIdx in fstBlkIdx..lstBlkIdx) {
val data = mfc.readBlock(blockIdx)
Log.d("NFC", "Read Successfully (Sector ${i}, Block ${blockIdx}): ${data.toHexString()}")
}
} else {
Log.e("NFC", "Auth Failed (Sector ${i}):Key is wrong or sector is locked")
}
}
}
0x20 -> Log.e("NFC_DIAG", "This is a ISO-DEP (CPU card),you must be to send APDU cmd")
0x00, 0x44 -> Log.e("NFC_DIAG", "This is a Ultralight/NTAG")
}
}
}
private fun ByteArray.toHexString() = joinToString("") { "%02X".format(it) }
override fun onResume()
{
super.onResume()
val intent = Intent(this, javaClass).addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP)
val pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_MUTABLE)
val filters = arrayOf(IntentFilter(NfcAdapter.ACTION_TECH_DISCOVERED))
val techList = arrayOf(arrayOf(NfcA::class.java.name))
nfcAdapter?.enableForegroundDispatch(this, pendingIntent, filters, techList)
}
override fun onPause()
{
super.onPause()
nfcAdapter?.disableForegroundDispatch(this)
}
Write Card
Because the functionality I wrote needs to improve speed and reduce reverse engineering costs, and it uses some key algorithms, I’m only providing the JNI C/C++ code here.
Let’s write code.
build.gradle.kts
android {
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
version = "3.31.3"
// This is your cmake txt file path.
path("src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt")
}
}
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.31.3)
set(CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET hidden)
set(CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN ON)
project(Test)
find_library(
log-lib
log
)
add_library(
Test
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file.
src/main.cpp
)
target_link_libraries(
Test
android
z
${log-lib}
${android-lib}
)
main.cpp
Note: Functions like generate_derived_key and lock_sector_by_kd are custom business logic and need to be implemented by yourself.
#include <jni.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
// We need some functions to convert JNI type to C/C++ type.
std::vector<uint8_t> jbyteArray_to_vector_uint_8(JNIEnv *env, jbyteArray array) {
jsize length = env->GetArrayLength(array);
std::vector<uint8_t> result(length);
env->GetByteArrayRegion(array, 0, length, reinterpret_cast<jbyte*>(result.data()));
return result;
}
std::string jcharArray_to_string(JNIEnv *env, jcharArray array) {
jsize length = env->GetArrayLength(array);
std::vector<jchar> chars(length);
env->GetCharArrayRegion(array, 0, length, chars.data());
return {chars.begin(), chars.end()};
}
static jboolean perform_auth(JNIEnv *env, jobject mifare_obj, const char* method_name,
int sector, const std::vector<uint8_t>& key) {
// method_name for example: authenticateSectorWithKeyA, authenticateSectorWithKeyB
// sector: Sector number/index
// key: Here is your correct key, if use default key, please set to [0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF]
jclass mifare_class = env->GetObjectClass(mifare_obj);
// public boolean authenticateSectorWithKeyA/authenticateSectorWithKeyB(int, byte[])
jmethodID auth_id = env->GetMethodID(mifare_class, method_name, "(I[B)Z");
// Create Kotlin/Java's byte array to store key
jbyteArray j_key = env->NewByteArray(6);
// Set data
env->SetByteArrayRegion(j_key, 0, 6, (const jbyte*)key.data());
// Call method
jboolean result = env->CallBooleanMethod(mifare_obj, auth_id, sector, j_key);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
env->ExceptionClear();
result = JNI_FALSE;
}
// Delete Kotlin/Java's local thread method ref
env->DeleteLocalRef(j_key);
env->DeleteLocalRef(mifare_class);
return result;
}
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jboolean JNICALL
/**
* Here declared a Kotlin method impl.
* You should change package_name and ClassName and methodName to ur really * name. For example: org.sgtu.test.Test#writeNfc -> Java_org_sgtu_test_Test_writeNfc()
*
* Tip: This is a code snippet from part of my code.
*/
Java_package_name_ClassName_methodName(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz,
jobject mifare_obj, jint sector_number,
jbyteArray seed, jcharArray uid, jbyteArray fst_kd) {
// If `mifare_obj` is a local reference passed in from Kotlin, it cannot be used across threads
// sector_number: Sector number/index, 0 - 15
// seed: Data to be written
// uid: Card id
// fst_kd: These are the variables required by my program; no need to pay attention
// env variable is from Kotlin or Java's entry point
// mifare_obj variable is `MifareClassic.get(tag)`
jclass mifare_class = env->GetObjectClass(mifare_obj);
// Get Kotlin/Java's method: public int sectorToBlock(int), this method used for get first data block index
jmethodID get_fst_blk_idx_id = env->GetMethodID(mifare_class, "sectorToBlock", "(I)I");
// Get Kotlin/Java's method: public void writeBlock(int, byte[]), this method used for write data to spec data block
// Data length must be to 16 byte (1 data block)
jmethodID write_id = env->GetMethodID(mifare_class, "writeBlock", "(I[B)V");
// Get first block index with sector number
jint fst_blk_idx = env->CallIntMethod(mifare_obj, get_fst_blk_idx_id, sector_number);
// Convert jbyteArray to std::vector<uint8_t>
std::vector<uint8_t> fst_kd_vector = jbyteArray_to_vector_uint_8(env, fst_kd);
// Convert jcharArray to std::string
std::string uid_str = jcharArray_to_string(env, uid);
// Generate a second derived key with first derived key and card id
std::vector<uint8_t> kd = generate_derived_key(fst_kd_vector, uid_str);
// Create Kotlin/Java's byte array to store second derived key
jbyteArray j_kd = env->NewByteArray(6);
// Set data
env->SetByteArrayRegion(j_kd, 0, 6, (jbyte*)kd.data());
// Authentication sector with perform_auth (Many authentication attempts are omitted here. You can directly refer to the implementation of perform_auth.)
jboolean is_auth = try_to_auth_sector(env, mifare_obj, sector_number, kd);
// Create a write flag variable
jboolean success = JNI_FALSE;
if (is_auth) {
// Use write method to write data into the spec data block
env->CallVoidMethod(mifare_obj, write_id, fst_blk_idx, seed);
// Check exception
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
env->ExceptionDescribe();
env->ExceptionClear();
success = JNI_FALSE;
} else {
// Lock the sector using a derived key (For detailed operating steps, please refer to the image above.)
success = lock_sector_by_kd(env, thiz, mifare_obj, write_id, fst_blk_idx + 3, fst_kd_vector, uid_str);
}
}
// Clear variable values
std::fill(kd.begin(), kd.end(), 0);
// Delete Kotlin/Java's local thread method ref
env->DeleteLocalRef(j_kd);
env->DeleteLocalRef(mifare_class);
// Return result
return success;
}